

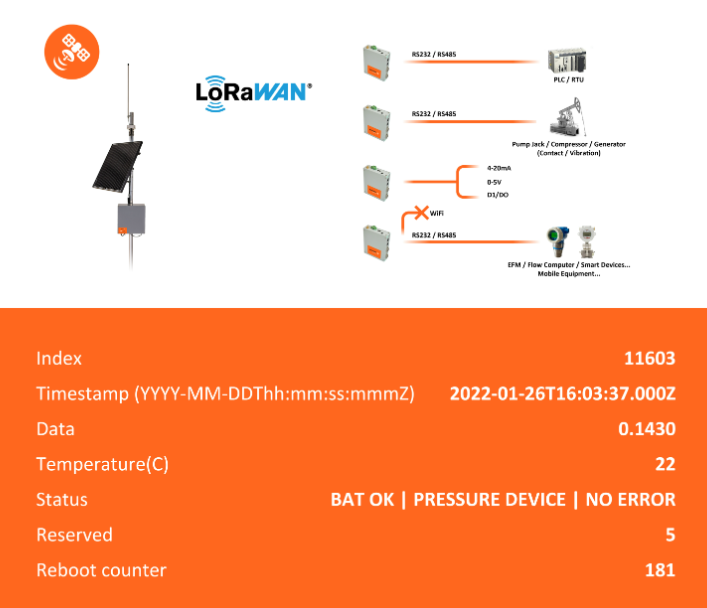
SCADA Protocols Such as Modbus or HART Can Send Uplinks and Receive Downlink Commands Over LoRaWAN® and Satellite Private Networks Using the MF GATEWAY and Battery Powered SCADA to LoRaWAN® Converter Nodes (Download Data Sheets for MF GATEWAY and MF GATEWAY ATEX).
LoRaWAN® and Satellite transmission offer SCADA systems key benefits
Advantages to using the above LoRaWAN® and Satellite network with SCADA devices versus traditional SCADA wired to satellite M2M solutions include:
- SCADA devices do not need individual satellite terminals per device with associated power requirements and costs
- SCADA devices do not need satellite line of sight (LOS)
- SCADA to LoRaWAN® converter nodes have long battery lives of up to 10 years with no solar panels required for autonomous power
- SCADA to LoRaWAN® converter nodes can be ATEX Zone 1 certified as they are extremely low power devices
- A single MF GATEWAY can provide connectivity for up to 4000 SCADA field devices for different and evolving use case requirements
SCADA Modbus over LoRaWAN® and Satellite Data Flow:
- Set of Modbus devices connected by an RS-485 to LoRaWAN® node which functions as a Modbus Master
- A Modbus master holds remotely configurable profiles with data collection periodicity, device address and Modbus function codes
- Data collection starts automatically and periodically. At every wake-up, the LoRaWAN® converter node transmits the Modbus commands to the Modbus connected devices. The response of the Modbus connected devices is transmitted over LoRaWAN®.
- The LoRaWAN® uplink is received by the listening MF GATEWAY unit over a distance of up to 5km (read more about the MF GATEWAY product).
- The MF GATEWAY runs an edge LoRaWAN® Network Server (LNS) which receives the LoRaWAN® uplink and sends the LoRaWAN® node any required acknowledgement or queued downlink commands with an extremely low latency (LoRaWAN® nodes only receive downlinks immediately after an uplink is made to preserve power and extend battery life)
- The MF Gateway gathers uplink payloads from many field devices. These uplinks are bundled together to be transmitted in a store and forward manner via the MinFarm optimized satellite protocol architecture over MF GATEWAY L-band satellite link
- Satellite data is sent over a geostationary satellite to a managed service Teleport REST API (read more about MinFarm satellite connectivity over L-band)
- The MinFarm REST API server, running on a private network hosted server, calls the Teleport REST API to retrieve bundled payload uplinks and send waiting command downlinks. This call is made from inside a customer’s private network and behind the customer’s firewall (read more about the MinFarm REST API and security architecture)
- The MinFarm REST API unpacks the SCADA field device payloads and forwards the raw data to a customer designated endpoint on the customer network such as a SCADA server
- The SCADA server user interface presents the remote field device data to a control operator and allows command downlinks to be transmitted
The field device can be located anywhere in the world. A similar process takes place for the HART protocol connected to a HART to LoRaWAN® converter node.
